An array is a group of variables which all have the same elementary data type and that are grouped together, one after the other, in a continuous data block. In the program you can either use the whole array or individual array elements via index (constant, variable index, result of expression).
Declaration
To declare ARRAY type variables in the POU header use the following syntax:
ARRAY[A...B,C...D,E...F] OF <data type> where:
A= |
first element index |
first dimension |
B= |
last element index |
|
C= |
first element index |
second dimension (optional) |
D= |
last element index |
|
E= |
first element index |
third dimension (optional) |
F= |
last element index |
Arrays can be 1, 2 or 3-dimensional. In each dimension, an array can have several fields. Element indexes are positive or negative integers. The first element must be smaller than the last element.
An array cannot be used as a variable by another array.
When accessing an index of an array, Control FPWIN Pro7 does not check the index against the bounds of the array. Make sure the index lies within the range defined in the POU header.
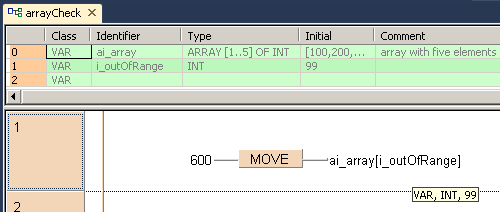
Example: ARRAY [1..5] OF INT
In this example, ai_array[99] is out of range but does not produce an error message.
Data types valid for arrays are:
BOOL
DATE
DATE_AND_TIME
DINT
DWORD
INT
REAL
STRING
TIME
TIME_OF_DAY
UDINT
UINT
WORD
Data Unit Type (DUT)
- Do not assign addresses unless you have to! Provide addresses for PLC inputs and outputs (X, Y) or if access to certain memory areas is required.
- The compiler automatically assigns addresses after the power has been turned on. This prevents errors caused by duplicate outputs and ensures that the addresses are automatically updated when the PLC type is changed.
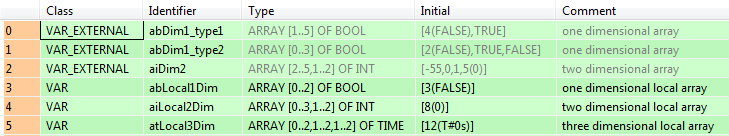
Example 1: Different arrays declared in the global variable list
E.g., array_1d_BOOL0 is a one-dimensional array with five elements. Use index 2 (array_1d_BOOL0[1]) to access the first element and index 5 (array_1d_BOOL0[5]) to access the last element.
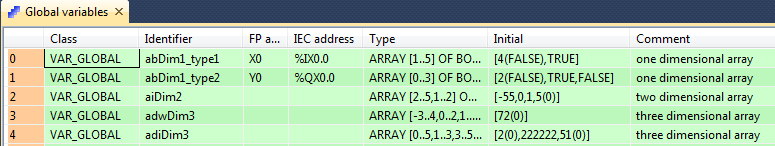
Example 2: Different arrays declared in the POU header