


 FNS_InitConfigDataTable
FNS_InitConfigDataTableConfigure data for FP-FNS blocks
The FNS_InitConfigDataTable function creates a ConfigDataTable from the variable ProcessDataTable, which can be a single-element data type or a multi-element data type. This ConfigDataTable is necessary to configure the FP-FNS block using the function block FNS_ProfibusDP, FNS_DeviceNet, FNS_CANopen and FNS_ProfinetIO.

Input
Input and output of process data variables
Output
Configuration data for FP-FNS blocks. The array size of the variable ConfigDataTable has to correspond to the number of elements of the ProcessDataTable variable.
Make sure that the size of the variable ConfigDataTable corresponds to the structure of the variable ProcessDataTable, e.g. if ProcessDataTable consists of three entries, then ConfigDataTable has to be an "Array[0..2] of WORD" with a size that matches the number of entries. If ProcessDataTable has only one entry (e.g. WORD), then ConfigDataTable has to be an "Array[0..0] of WORD" (with size 1).
Allowed data types for the input of the FNS_InitConfigDataTable are all 16-bit (INT, WORD), 32-bit (DINT, DWORD, TIME (32 bits), REAL) and 64-bit variables or arrays of them. 64-bit variables are defined as 2-dimensional arrays, e.g. "Array[0..0,0..3] of INT" is a 64-bit variable, while "Array[0..3] of INT" represents an array with four elements of 16-bit variables.
The data types BOOL, STRING and arrays of these types are NOT allowed at the input of the function FNS_InitConfigDataTable.
The output ConfigDataTable of the function must be an array of WORD.
The following syntax table shows how to declare 16-bit, 32-bit and 64-bit variables and arrays thereof when using them as ProcessDataTable input for the FNS_InitConfigDataTable function.
Input Data type |
Size of Input |
Comment |
|---|---|---|
INT, WORD |
16-bit |
|
DINT, WORD, REAL, TIME |
32-bit |
|
Array[0..0,0..3] of INT Array[0..0,0..3] of WORD |
64-bit |
2-dimensional array; size of second dimension = 4 |
Array[a ..b] of INT/Array[a ..b] of WORD |
Array of 16-bit Size = b-a+1 |
1-dimensional array |
Array[a ..b] of DINT/Array[a ..b] of DWORD/ Array[a ..b] of REAL/Array[a ..b] of TIME |
Array of 32-bit Size = b-a+1 |
1-dimensional array |
Array[0..x,0..3] of INT Array[0..x,0..3] of WORD |
Array of 64-bit Size = x+1 |
2-dimensional array; size of second dimension = 4 |
For each element of the DUT applied at ProcessDataTable, an element in the WORD array at ConfigDataTable is generated according to the following formula:
enum class enumFnsDataTypeCode : int
{
INVALID = -1,
SIGNED_16 = 0x02,
SIGNED_32 = 0x03,
UNSIGNED_16 = 0x05,
UNSIGNED_32 = 0x06,
UNSIGNED_64 = 0x11,
REAL_32 = 0x12
};Low byte: data type code required for FNS
High byte: number of elements in case of an array
In the global variable list you define variables that can be accessed by all POUs in the project.

In this example, the variable ProcessData is a DUT of the type ProcessDataStructure with the following structure:
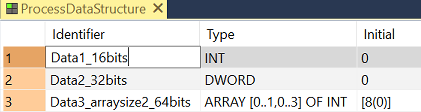
As the DUT has three entries, the output variable ConfigData has to be an array of WORD with a size of three (e.g.: Array [0..2] of WORD).
All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header. The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
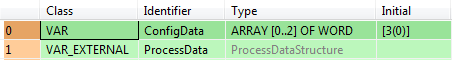
VAR
ConfigData: ARRAY [0..2] OF WORD:=[3(0)];
END_VAR
VAR_EXTERNAL
ProcessData: ProcessDataStructure;
END_VARThe size of the variable ConfigDataTable has to correspond to the number of entries of the input variable ProcessData.
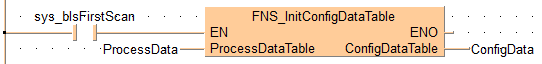
When sys_bIsFirstScan is TRUE, i.e. in the first cycle, the function is executed. The value of the variable ConfigData corresponds to the structure of the input variable ProcessData, its number and type of elements.
BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
ACTIVE_NETWORK := 0 ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 5 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_VARIN,,ProcessData,11,2,13,4,);
B(B_VAROUT,,ConfigData,29,2,31,4,);
B(B_F,E_FNS_InitConfigDataTable!,,13,0,29,4,,?DEN?dProcessDataTable?AENO?cConfigDataTable);
B(B_CONTACT,,sys_bIsFirstScan,5,1,7,3,);
L(1,2,5,2);
L(7,2,13,2);
L(1,0,1,5);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODYIf sys_bIsFirstScan then
ConfigData:=FNS_InitConfigDataTable(ProcessData);
end_if;