


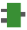 F146_READ_DATA
F146_READ_DATARead data from slave
Use this instruction to request data from a slave via the communication port using the MEWTOCOL-COM or Modbus RTU protocol, as defined in the system registers of the port used.Make sure the same protocol is set for master and slave.Master and slave must have matching memory areas. If the slave data is not available in the user area of the master, use F146_READ_DATA_TYPE_OFFS or F145F146_MODBUS_MASTER.
For data transmissions using the Modbus protocol, the compiler generates Modbus commands based on the Modbus reference numbers.
Input
Specifies the communication ports depending on the PLC type:
COM port e.g. SYS_COM0_PORT
Ethernet port e.g. SYS_ETHERNET_USER_CONNECTION_1
MCU/SCU e.g. 16#xx01 (xx = slot number) in COM01
Station number of the slave (MEWTOCOL: 1–99, MODBUS: 1–255)
Set to 1, if a SYS_ETHERNET_USER_CONNECTION_xx is applied to input Port
Source address on the slave from which the data is requested.
Output
Word area or register on the master unit to which the requested data is written.
Instead of using this F instruction, we recommend using the most flexible instruction:FP_READ_FROM_SLAVE_AREA_OFFS.
The F145 or F146 instructions can only be executed if neither instruction is active. Evaluate the "F145/F146 not active" flag in your program to check the state of the instructions.
Evaluate the "F145/F146 error" flag to check whether transmission has completed normally or with an error.
The F145 or F146 instructions cannot be executed if the destination address is a special internal flag (from R9000), a special data register (from DT9000/DT90000), or a file register FL.
In the global variable list you define variables that can be accessed by all POUs in the project.


All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header. The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
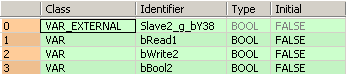
VAR
bBool2: BOOL:=FALSE;
bRead1: BOOL:=FALSE;
bWrite2: BOOL:=FALSE;
END_VAR
VAR_EXTERNAL
Slave2_g_bY38: BOOL:=FALSE;
END_VAR
VAR
END_VARIf bRead1 and sys_bIsComPort1F145F146NotActive are set to TRUE, the global variable Slave2_g_bY38, which is assigned to Y38 of slave 2, is read and stored in bBool2.

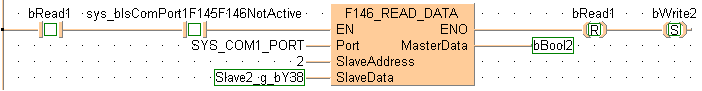
BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
ACTIVE_NETWORK := 0 ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 6 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_CONTACT,,sys_bIsComPort1F145F146NotActive,8,1,10,3,);
B(B_CONTACT,,bWrite2,18,1,20,3,);
B(B_VARIN,,SYS_COM1_PORT,21,2,23,4,);
B(B_VARIN,,2,21,3,23,5,);
B(B_VARIN,,Slave2_g_bY38,21,4,23,6,);
B(B_VAROUT,,bBool2,33,2,35,4,);
B(B_COIL,,bWrite2,36,1,38,3,E);
B(B_COIL,,bRead1,42,1,44,3,S);
B(B_F,F146_READ_DATA!,Instance,23,0,33,6,,?DEN?DPort?DSlaveAddress?DSlaveData?AENO?CMasterData);
L(1,2,8,2);
L(10,2,18,2);
L(38,2,42,2);
L(33,2,36,2);
L(20,2,23,2);
L(1,0,1,6);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODY
if (bRead1 and sys_bIsComPort1F145F146NotActive) then
F146_READ_DATA(Port := SYS_COM1_PORT,
SlaveAddress := 2,
SlaveData := Slave2_g_bY38,
MasterData => bBool2);
bRead1 := false;
bWrite1 := true;
end_if;