


 TO_INT
TO_INTOverloaded conversion to INTEGER
This instruction converts a value of any allowed data type into a value of the data type INT.
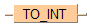
Input
Value to be converted
Output
Conversion result

All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header. The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
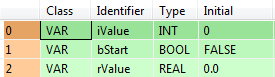
VAR
iValue: INT:=0;
bStart: BOOL:=FALSE;
rValue: REAL:=0.0;
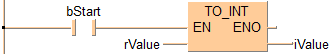
END_VARWhen the variable bStart is set to TRUE, the function is carried out.

BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
ACTIVE_NETWORK := 0 ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 4 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_VARIN,,rValue,10,2,12,4,);
B(B_VAROUT,,iValue,18,2,20,4,);
B(B_F,E_TO_INT!,,12,0,18,4,,?DEN?D?AENO?C);
B(B_CONTACT,,bStart,5,1,7,3,);
L(1,2,5,2);
L(7,2,12,2);
L(1,0,1,4);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODY
IF (bStart) THEN
iValue := TO_INT(rValue);
END_IF;