


 FP_ASCII_TO_HEX
FP_ASCII_TO_HEXASCII -> HEX conversion
This FP instruction converts the hexadecimal ASCII HEX codes at s_Start to hexadecimal characters if the trigger EN is TRUE. n_Chars specifies the number of bytes to be converted.The result is stored in d.
ASCII code requires 8 bits (1 byte) to express one hexadecimal character.Upon conversion, the data length will thus be half the length of the ASCII code source data.
Input
Starting address
Number of bytes
Output
Converted bytes
Two characters of ASCII code are converted into two one-byte numerical digits. In this process, higher-level characters and lower-level characters are exchanged. Four characters are converted as one segment of data.

ASCII HEX codes to express hexadecimal characters:
Hexadecimal character |
ASCII HEX code |
|---|---|
0123456789ABCDEF |
16#3016#31 16#32 16#33 16#34 16#35 16#36 16#37 16#38 16#39 16#41 16#42 16#43 16#44 16#45 16#46 |
if the area specified using the index modifier exceeds the limit.
if the number of bytes specified by n_Chars is greater than the area specified by s_Start
if the conversion result is greater than the data area specified by d
if n_Chars = 0
if ASCII characters other than 0–F are specified
if the area specified using the index modifier exceeds the limit.
if the number of bytes specified by n_Chars is greater than the area specified by s_Start
if the conversion result is greater than the data area specified by d
if n_Chars = 0
if ASCII characters other than 0–F are specified
Offset |
ASCII codes |
Hex. equivalent |
Offset |
Converted hex. characters |
|||
s1_Start |
0 |
16#4241 |
BA |
Þ |
d |
0 |
16#CDAB |
1 |
16#4443 |
DC |
1 |
||||
n_Chars |
0 |
16#0004 |
2 |
||||
1 |
3 |
Offset |
ASCII codes |
Hex. equivalent |
Offset |
Converted hex. characters |
|||
s1_Start |
0 |
16#4241 |
BA |
Þ |
d |
0 |
16#CDAB |
1 |
16#4443 |
DC |
1 |
||||
n_Chars |
0 |
16#0004 |
2 |
||||
1 |
16#0000 |
3 |
|||||
2 |
4 |
Offset |
ASCII codes |
Hex. equivalent |
Offset |
Converted hex. characters |
|||
s1_Start |
0 |
16#3231 |
21 |
Þ |
d |
0 |
16#3412 |
1 |
16#3433 |
43 |
1 |
16#7856 |
|||
2 |
16#3635 |
65 |
2 |
||||
3 |
16#3837 |
87 |
3 |
||||
n_Chars |
0 |
16#0008 |
4 |
||||
1 |
5 |
If an odd number of characters is being converted, 0 will be entered for bit position 0–3 of the last converted byte.
Offset |
ASCII codes |
Hex. equivalent |
Offset |
Converted hex. characters |
|||
s1_Start |
0 |
16#3231 |
21 |
Þ |
d |
0 |
16#3412 |
1 |
16#3433 |
43 |
1 |
16#7056 |
|||
2 |
16#3635 |
65 |
2 |
||||
3 |
16#3837 |
87 |
3 |
||||
n_Chars |
0 |
16#0007 |
4 |
||||
1 |
5 |

All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header. The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
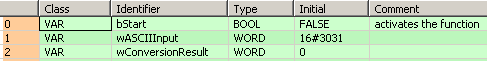
VAR
bStart: BOOL:=FALSE;
(*activates the function*)
wASCIIInput: WORD:=16#3031;
wConversionResult: WORD:=0;
END_VARWhen the variable bStart is set to TRUE, the function is carried out.


BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
ACTIVE_NETWORK := 0 ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 6 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_CONTACT,,bStart,5,2,7,4,);
B(B_VARIN,,wASCIIInput,11,3,13,5,);
B(B_VARIN,,2,11,4,13,6,);
B(B_VAROUT,,wConversionResult,23,3,25,5,);
B(B_F,FP_ASCII_TO_HEX!,,13,1,23,6,,?DEN?Ds_Start?Dn_Chars?AENO?Cd);
L(1,3,5,3);
L(7,3,13,3);
L(1,0,1,6);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODY
If (bStart) then
FP_ASCII_TO_HEX(s_Start := wASCIIInput,
n_Chars := 2,
d => wConversionResult);
End_if;