


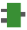 FP_BCC
FP_BCCBlock check character calculation
This FP instruction calculates the block check character (BCC) according to the calculation specified by s1_Control. The data is specified by the start address s2_Start and the number of bytes n_Bytes. The BCC is stored in the 16-bit area specified by d.
Input
Calculation method
Starting address
Number of bytes
Output
Block check character
Specifying the control code s1_Control

0: Addition (SYS_BCC_CALCULATION_METHOD_ADD)
1: Subtraction (SYS_BCC_CALCULATION_METHOD_SUB)
2: Exclusive OR (SYS_BCC_CALCULATION_METHOD_XOR)
16#A: CRC-16 (SYS_BCC_CALCULATION_METHOD_CRC16)
16#0–16#F
0: Binary data (1 byte)
1: ASCII data (2 bytes)
if the area specified using the index modifier exceeds the limit.
if the area specified using the index modifier exceeds the limit.

All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header.The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
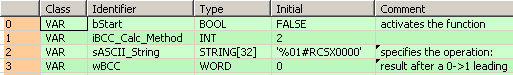
VAR
bStart: BOOL:=FALSE;
(*activates the function*)
iBCC_Calc_Method: INT:=2;
sASCII_String: STRING[32]:='%01#RCSX0000';
(*specifies the operation:
0: addition
1: subtraction
2:XOR*)
wBCC: WORD:=0;
(*result after a 0->1 leading
edge from start: 10#172*)
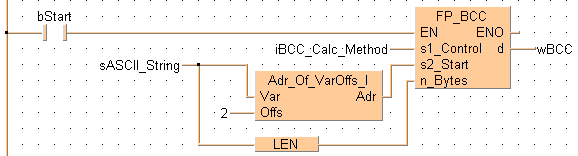
END_VARWhen bStart turns to TRUE, a block check character calculation is performed on sASCII_String. The calculation method is exclusive OR. (Use this method when large amounts of data are transmitted).
Exclusive OR operation:
bvar_1 |
bvar_2 |
bvar_3 |
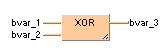 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
0 |
The binary codes of the first two characters are compared with each other to yield an 8-character exclusive OR operation result. This result is then compared to the binary code of the next character, and so on until the final character is reached. The last exclusive OR result is the block check character.
BCC calculation using exclusive OR operation:


BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
ACTIVE_NETWORK := 0 ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 11 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_CONTACT,,bStart,3,2,5,4,);
B(B_VARIN,,iBCC_Calc_Method,24,3,26,5,);
B(B_F,Adr_Of_VarOffs_I!,,16,5,25,9,,?D@'Var'?DOffs?CAdr);
B(B_VAROUT,,wBCC,33,3,35,5,);
B(B_VARIN,,sASCII_String,11,4,13,6,);
B(B_VARIN,,2,14,7,16,9,);
B(B_F,LEN!,,16,8,21,11,,?DIN?C);
B(B_F,FP_BCC!,,26,1,33,7,,?DEN?Ds1_Control?Ds2_Start?Dn_Bytes?AENO?Cd);
L(16,5,16,7);
L(13,5,16,5);
L(13,5,13,10);
L(13,10,16,10);
L(25,5,25,7);
L(25,5,26,5);
L(26,6,26,10);
L(21,10,26,10);
L(5,3,26,3);
L(1,3,3,3);
L(1,0,1,11);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODYIn this example, Adr_Of_VarOffs_I is used to create an offset of 2 words to compensate for the string's start code. By using LEN, the BCC calculation is performed on the entire data string.

IF bStart then
FP_BCC(s1_Control := iBCC_Calc_Method,
s2_Start := Adr_Of_VarOffs( Var:= sASCII_String, Offs:= 2),
n_Bytes := LEN( sASCII_String),
d => wBCC);
END_IF;