


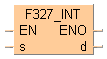
 F327_INT
F327_INTFloating point data -> 16-bit integer data (the largest integer not exceeding the floating point data)
The function converts a floating point data at input s in the range -32767.99 to 32767.99 into integer data (including +/- sign). The result of the function is returned at output d.
Input
Source REAL number data (2 words)
Output
Destination for storing converted data
The converted integer value at output d is always less than or equal to the floating point value at input s:
When there is a positive floating point value at the input, a positive pre-decimal value is returned at the output.
When there is a negative floating point value at the input, the next smallest pre-decimal value is returned at the output.
If the floating point value has only zeros after the decimal point, its pre-decimal point value is returned.
if the value at input s is not a REAL number, or the converted result exceeds the 16-bit area at output d.
if the value at input s is not a REAL number, or the converted result exceeds the 16-bit area at output d.
if the calculated result is 0.

All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header. The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
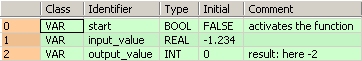
VAR
start: BOOL:=FALSE;
(*activates the function*)
input_value: REAL:=-1.234;
output_value: INT:=0;
(*result after a 0->1 leading
edge from start: 32*)
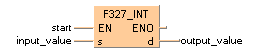
END_VARIn this example, the input variable input_value is declared. However, you can write a constant directly at the input contact of the function instead.
When the variable start is set to TRUE, the function is carried out. It converts the floating point value -1.234 into the whole number value -2, which is transferred to the variable output_value. Since the whole number may not exceed the floating point value, the function rounds down here.

BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
ACTIVE_NETWORK := 0 ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 5 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_VARIN,,output,7,1,9,3,);
B(B_VARIN,,input_value,7,2,9,4,);
B(B_VAROUT,,output_value,17,2,19,4,);
B(B_F,F327_INT,,9,0,17,4,,?DEN?D@'s'?AENO?Cd);
L(1,0,1,5);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODY
IF start THEN
F327_INT(input_value, output_value);
END_IF;