


 MOVE
MOVEMove value to specified destination
MOVE assigns the unchanged value of the input variable to the output variable.

Input
Source
Output
Output as input
Destination
When using the data type STRING with small PLCs like FP-e or FP0, make sure that the length of the result string is equal to or greater than the length of the source string.
In LD/FBD editor this instruction can be expanded, see also modifying elements.

All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header. The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
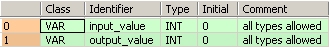
VAR
input_value: INT:=0;
(*all types allowed*)
output_value: INT:=0;
(*all types allowed*)
END_VARIn this example the input variable input_value has been declared. Instead, you may enter a constant directly at the input contact of a function.
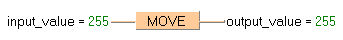
Input_value is assigned to output_value without being modified.

BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
ACTIVE_NETWORK := 0 ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 2 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_F,MOVE!,Instance,9,0,14,2,,?D?C);
B(B_VARIN,,input_value,7,0,9,2,);
B(B_VAROUT,,output_value,14,0,16,2,);
L(1,0,1,2);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODY
output_value:= input_value;LD |
input_value |
MOVE |
|
ST |
output_value |