


 F115_FIFT
F115_FIFTFIFO buffer area definition
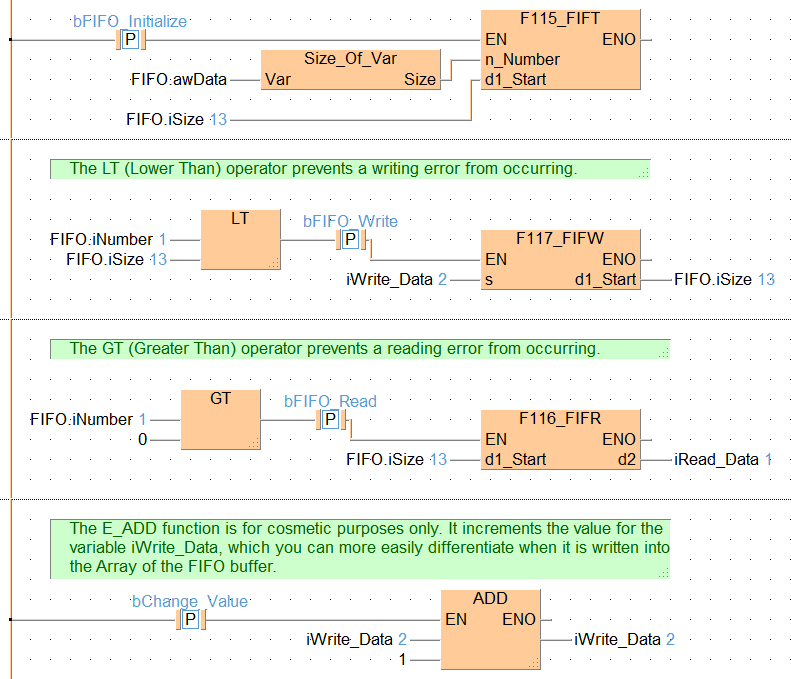
F115 specifies the starting area d1_Start for the FIFO (First-In-First-Out) buffer and the memory size n_Number of the FIFO buffer.

Input
specifies the memory size of FIFO buffer
range: 1–256
starting 16-bit area of FIFO buffer
Instead of using this F instruction, we recommend using the corresponding FP7 instruction: FP_FIFO_DEFINE, FP_LIFO_DEFINE
Definition of the area using the FIFT instruction should be carried out only once, before writing to or reading from the FIFO buffer. When the FIFT instruction is executed, the FIFO buffer area is defined as follows:

When the FIFT instruction is executed, the following are stored as default values: d1_Start = n_Number (the value specified by the FIFT instruction), d1_Start + 1 = 0, and d1_Start + 2 = 16#0000.
if n_Number = 0
if n_Number > 256
if the area specified by n_Number exceeds the limit
if n_Number = 0
if n_Number > 256
if the area specified by n_Number exceeds the limit
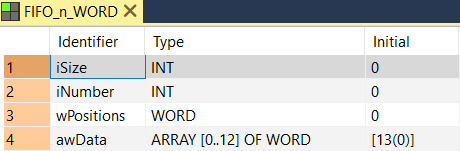

All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header. The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
VAR
FIFO: FIFO_n_WORD;
iRead_Data: INT:=0;
iWrite_Data: INT:=1;
bFIFO_Initialize: BOOL:=FALSE;
bFIFO_Write: BOOL:=FALSE;
bFIFO_Read: BOOL:=FALSE;
bChange_Value: BOOL:=FALSE;
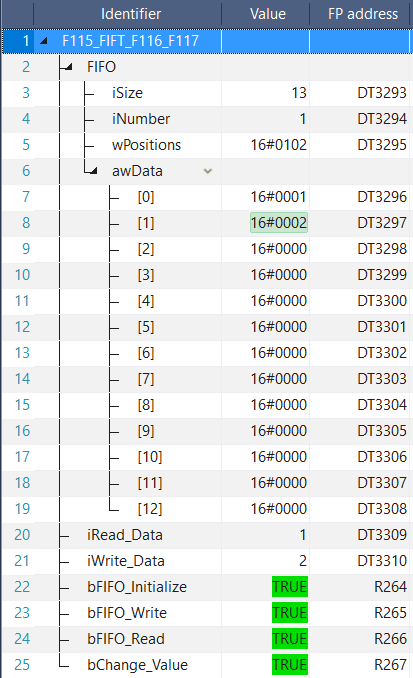
END_VARThe example below illustrates the status of the buffer after bFIFO_Write has been enabled twice and bFIFO_Read once. When bFIFO_Write was activated the first time, the value 1 was written into FIFO.awData[0]. When bFIFO_Read was enabled, iRead_Data then read this value. When bFIFO_Write was enabled the second time, the writing pointer was incremented by one and the value 2 written into FIFO.awData[1]. see Entry Data Monitor 1

BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 7 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_CONTACT,,bFIFO_Initialize,6,1,8,3,R);
B(B_F,F115_FIFT,,24,0,33,5,,?DEN?Dn?Dd1?AENO);
B(B_VARIN,,FIFO.awData,11,3,13,5,);
B(B_F,Size_Of_Var,,13,2,23,5,,?D@'Var'?CSize);
B(B_VARIN,,FIFO.iSize,11,5,13,7,);
L(1,0,1,7);
L(1,2,6,2);
L(8,2,24,2);
L(23,3,24,3);
L(23,3,23,4);
L(24,4,24,6);
L(13,6,24,6);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 9 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_COMMENT,,The LT (Lower Than) operator prevents a writing error from occurring.,3,1,33,2,);
B(B_VARIN,,FIFO.iNumber,8,4,10,6,);
B(B_F,@LT-2,,10,3,15,7,,?D?D?C);
B(B_CONTACT,,bFIFO_Write,17,4,19,6,R);
B(B_VARIN,,FIFO.iSize,8,5,10,7,);
B(B_F,F117_FIFW,,24,4,33,8,,?DEN?D@'s'?AENO?Cd1);
B(B_VARIN,,iWrite_Data,22,6,24,8,);
B(B_VAROUT,,FIFO.iSize,33,6,35,8,);
L(1,0,1,9);
L(15,5,17,5);
L(19,5,19,6);
L(19,6,24,6);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 9 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_COMMENT,,The GT (Greater Than) operator prevents a reading error from occurring.,3,1,34,2,);
B(B_VARIN,,FIFO.iNumber,7,4,9,6,);
B(B_F,@GT-2,,9,3,14,7,,?D?D?C);
B(B_CONTACT,,bFIFO_Read,16,4,18,6,R);
B(B_VARIN,,0,7,5,9,7,);
B(B_F,F116_FIFR,,24,4,33,8,,?DEN?Dd1?AENO?Cd2);
B(B_VARIN,,FIFO.iSize,22,6,24,8,);
B(B_VAROUT,,iRead_Data,33,6,35,8,);
L(1,0,1,9);
L(14,5,16,5);
L(18,5,18,6);
L(18,6,24,6);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 9 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_COMMENT,,The E_ADD function is for cosmetic purposes only. It increments the value for the variable iWrite_Data~ which you can more easily differentiate when it is written into the Array of the FIFO buffer.,3,1,34,4,);
B(B_CONTACT,,bChange_Value,9,5,11,7,R);
B(B_F,E_ADD-2,,22,4,28,9,,?DEN?Da_NumN?Da_NumN?AENO?C);
B(B_VARIN,,iWrite_Data,20,6,22,8,);
B(B_VAROUT,,iWrite_Data,28,6,30,8,);
B(B_VARIN,,1,20,7,22,9,);
L(1,0,1,9);
L(1,6,9,6);
L(11,6,22,6);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODY
IF DF(bFIFO_Initialize) THEN
(* Create the FIFO buffer *)
F115_FIFT(n_Number := Size_Of_Var(FIFO.awData), d1_Start := FIFO.iSize);
REPEAT
(* Initialize FIFO buffer with values *)
iWrite_Data:=iWrite_Data+1;
F117_FIFW(s := iWrite_Data, d1_Start => FIFO.iSize);
UNTIL(FIFO.iNumber>=FIFO.iSize)
END_REPEAT;
END_IF;
IF DF( bFIFO_Write) THEN
(* Write value of Write_Data to FIFO buffer *)
(* at leading edge of FIFO_Write *)
F117_FIFW(s := iWrite_Data, d1_Start => FIFO.iSize);
END_IF;
IF DF(bFIFO_Read) THEN
(* Read value from FIFO buffer *)
(* at leading edge of FIFO_Read *)
F116_FIFR(d1_Start := FIFO.iSize, d2 => iRead_Data);
END_IF;