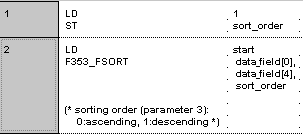
 F353_FSORT
F353_FSORTSort data in real number data table (floating point data table)
The function sorts values (with +/- sign) in a data table in ascending or descending order.
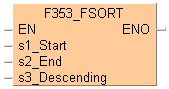
Input
starting area of data table to be sorted
ending area of data table to be sorted
specifies sorting order:
0 = ascending
1 = descending
Instead of using this F instruction, we recommend using the corresponding FP7 instruction: FP_DATA_SORT
Input s1_Start specifies the starting area of the data table, and s2_End specifies the end. You determine the sorting order at input s3_Descending.
At input s3_Descending you can enter the following values:
0 |
ascending order, i.e. begin with the smallest value |
1 |
descending order, i.e. begin with the largest value |
The data are sorted via bubble sort in the order specified according to the value entered at input s1. Since the number of word comparisons increases in proportion to the square of the number of words, the sorting process can take some time when there are a large number of words. When the value at inputs s1_Start=s2_End, no sorting takes place.
if the address of the variable at input s1_Start > s2_End
if the address areas of the values at inputs s1_Start and s2_End are different
if the floating point values exceed the processing range.
if the address of the variable at input s1_Start > s2_End
if the address areas of the values at inputs s1_Start and s2_End are different
if the floating point values exceed the processing range.

All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header. The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
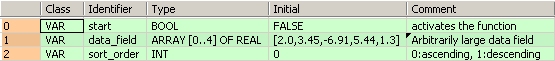
VAR
CalculateY: BOOL:=FALSE;
xValue: REAL:=4.0;
yValue: REAL:=0.0;
xyValues: XY_DUT;
END_VAR
VAR
CalculateY: BOOL:=FALSE;
xValue: REAL:=4.0;
yValue: REAL:=0.0;
xyValues: XY_DUT;
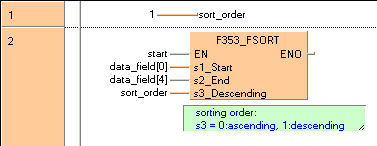
END_VARIn this example, the input variable sort_order is declared. However, you can write a constant (e.g. 1 for a descending sorting order) directly at the input contact of the function in the body.
When the variable start is set to TRUE, the function is carried out.
It sorts the elements of the ARRAY data_field in descending order.
BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
ACTIVE_NETWORK := 0 ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 3 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_VAROUT,,sort_order,9,0,11,2,);
B(B_VARIN,,1,7,0,9,2,);
L(1,0,1,3);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 9 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_VARIN,,output,8,1,10,3,);
B(B_F,F353_FSORT,,10,0,19,6,,?DEN?D@'s1'?Ds2?Ds3?AENO);
B(B_VARIN,,sort_order,8,4,10,6,);
B(B_VARIN,,data field[0],8,2,10,4,);
B(B_VARIN,,data field[4],8,3,10,5,);
B(B_COMMENT,,sorting order:ø^s3 = 0:ascending~ 1:descending,11,6,26,8,);
L(1,0,1,9);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODY
sort_order:=1;
IF start then
F353_FSORT( s1_Start:= data_field[0],
s2_End:= data_field[4],
s3_Descending:= sort_order);
END_IF;