


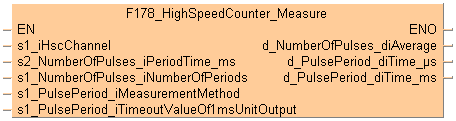
 F178_HighSpeedCounter_Measure
F178_HighSpeedCounter_MeasureInput pulse measurement
This instruction measures the number of input pulses in a specified counting period and the pulse period.
Input
High-speed counter channel: 0–5
Counting period [ms]:
1–5000 (1ms–5s).
Number of counting periods: 1–5
Unit of pulse period measurement
0: Pulse period is not measured
1: Pulse period is measured in ms
2: Pulse period is measured in ms
3: Pulse period is measured in ms and ms
Time-out value of pulse period measurement [ms]:
0: no time-out
1: 100ms
2: 200ms
3: 300ms
4: 500ms
Output
Average number of pulses per counting period (no. of pulses in counting period/number of counting periods)
Pulse periodm
Pulse period [ms]
For input pulse measurement, the channel number, the counting period (1ms–5s) and the number of counting periods (1–5) must be specified. These parameters are used to calculate the average number of input pulses per counting period.
The unit of pulse period measurement ([ms], [ms] or both) can be specified.
If the measurement is in ms, the pulse period is measured and output immediately upon execution of this instruction. A maximum of approx. 174.4ms can be measured.
If the measurement is in ms, the value of the pulse period is updated after every measurement. A maximum of approx. 49.7 days can be measured. A time-out value can be specified after which the measured pulse period is set to -1 if measurement has not been completed.
During the first counting periods after starting the instruction, the measured pulse period is set to -1 until the specified number of counting periods has been reached.
If the pulse period is longer than the measurable range or if measurement has not been completed, the measured pulse period is set to -1.
Select the high-speed counter input for the desired channel in the system registers.
Keep the execution condition TRUE for pulse measurement using this instruction.
To stop the measurement, turn the execution condition to FALSE.
When a high-speed counter instruction is executed, the high-speed counter control flag (e.g. sys_bIsHscChannel0ControlActive) for the channel used turns to TRUE. No other high-speed counter instruction using the same channel can be executed as long as the control flag is TRUE.
The instruction can be executed simultaneously on a maximum of two channels.
If both the main program and the interrupt program contain code for the same channel, make sure both are not executed simultaneously.
The status of the high-speed counter control flag or pulse output control flag may change while a scan is being carried out. For example, if the number of received bytes is read more than once different statuses may exist within one scan.
if the high-speed counter channel is already used by another high-speed counter or pulse output instruction
if the number of channels used is 3 or more
if the high-speed counter channel is already used by another high-speed counter or pulse output instruction
if the number of channels used is 3 or more

All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header. The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
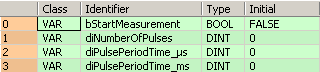
VAR
bStartMeasurement: BOOL:=FALSE;
diNumberOfPulses: DINT:=0;
diPulsePeriodTime_μs: DINT:=0;
diPulsePeriodTime_ms: DINT:=0;
END_VAR
BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
ACTIVE_NETWORK := 0 ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 9 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_F,F178_HighSpeedCounter_Measure!,Instance,25,1,53,9,,?DEN?Ds1_iHscChannel?Ds2_NumberOfPulses_iPeriodTime_ms?Ds1_NumberOfPulses_iNumberOfPeriods?Ds1_PulsePeriod_iMeasurementMethod?Ds1_PulsePeriod_iTimeoutValueOf1msUnitOutput?AENO?Ad_NumberOfPulses_diAverage?Ad_PulsePeriod_diTime_μs?Ad_PulsePeriod_diTime_ms);
B(B_VARIN,,0,23,3,25,5,);
B(B_VARIN,,10,23,4,25,6,);
B(B_VARIN,,5,23,5,25,7,);
B(B_VARIN,,SYS_F178_HSC_MEASUREMENT_μs_ms,23,6,25,8,);
B(B_VARIN,,0,23,7,25,9,);
B(B_VAROUT,,diNumberOfPulses,53,3,55,5,);
B(B_VAROUT,,diPulsePeriodTime_μs,53,4,55,6,);
B(B_VAROUT,,diPulsePeriodTime_ms,53,5,55,7,);
B(B_CONTACT,,bStartMeasurement,9,2,11,4,);
L(1,3,9,3);
L(11,3,25,3);
L(1,0,1,9);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODY
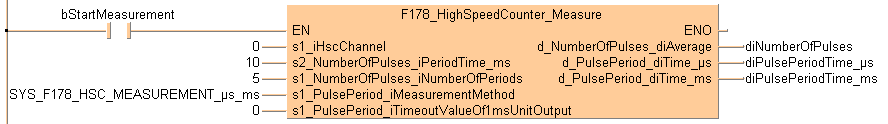
IF (bStartMeasurement) then
F178_HighSpeedCounter_Measure(s1_iHscChannel := 0,
s2_NumberOfPulses_iPeriodTime_ms := 10,
s1_NumberOfPulses_iNumberOfPeriods := 5,
s1_PulsePeriod_iMeasurementMethod := SYS_F178_HSC_MEASUREMENT_μs_ms,
s1_PulsePeriod_iTimeoutValueOf1msUnitOutput := 0,
d_NumberOfPulses_diAverage => diNumberOfPulses,
d_PulsePeriod_diTime_μs => diPulsePeriodTime_μs,
d_PulsePeriod_diTime_ms => diPulsePeriodTime_ms);
END_IF;