


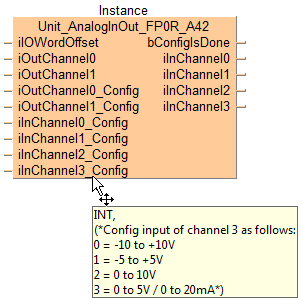
 Unit_AnalogInOut_FP0R_A42
Unit_AnalogInOut_FP0R_A42Function block to write to and read from an FP0R-A42 unit.
This function writes digital data to the analog output channels of the analog unit and reads converted digital data from its analog input channels. The digital values to be converted and output as analog values are specified at iOutChannel0 and iOutChannel1. The converted digital values from the analog unit are stored per channel in the output variables iInChannel0 to iInChannel3.
The analog output and input ranges are also set with this function block.
The voltage or current output must be set with the DIP switches.
Input
Set the offset of the first WX/WY address of the analog unit according to its installation position.
For analog expansion units connected directly to the CPU (without adapter): Use ExpansionUnitToIOWordOffset_FP0 or make the following settings: 2 (WX2/WY2) for unit number 1, 4 (WX4/WY4) for unit number 2, 6 (WX6/WY6) for unit number 3
For analog expansion units connected to the CPU via an adapter: Use ExpansionUnitToIOWordOffset_FPX_FP0 or select the offset from the table.
Unit position relative to the adapter |
Adapter position relative to the CPU |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1st unit |
2nd unit |
3rd unit |
4th unit |
5th unit |
6th unit |
7th unit |
8th unit |
|
1st unit |
30 |
40 |
50 |
60 |
70 |
80 |
90 |
100 |
2nd unit |
32 |
42 |
52 |
62 |
72 |
82 |
92 |
102 |
3rd unit |
34 |
44 |
54 |
64 |
74 |
84 |
94 |
104 |
Set the digital value to be converted and output by the analog unit.
Set the voltage or current range for the analog output channel.
Set the voltage or current range for the analog input channel.
Output
TRUE when I/O configuration is completed and the unit is ready.
Returns the converted digital data from the analog unit by channel.
DIP switches 1 and 2 must be ON to use 14-bit mode. DIP switch 3 is used to set voltage or current output for channel 0, DIP switch 4 is used to set voltage or current output for channel 1, and DIP switch 5 is used to turn averaging on or off.
The DIP switch settings will become effective when the power is turned from OFF to ON.
Channel 0 |
Channel 1 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Voltage output |
Current output |
Voltage output |
Current output |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
No averaging: Conversion data is set for the specified input contact point area for each A/D conversion, on each channel.
Averaging: On each channel, for each A/D conversion, the maximum and minimum values from the data of the last ten times are excluded, the data from the other eight times is averaged and the result is set.
No averaging |
Averaging |
|
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
The examples show the wiring for input channels 0 and 1 and output channel 0.
Voltage input |
Current input |
|---|---|
 Connect the input instrument between the IN/V and IN/COM terminals. |
 Connect the IN/V and IN/I terminals. Connect the input instrument between the bridge and the IN/COM terminal. |
Voltage output |
Current output |
|---|---|
 Connect the output instrument between the OUT/V and OUT/COM terminals. |
 Connect the output instrument between the OUT/I and OUT/COM terminals. |
-10V to +10V DC input or output |
-5V to +5V DC input or output |
0V to 5V DC input or output |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Digital value (INT) |
Analog value |
Digital value (INT) |
Analog value |
Digital value (INT) |
Analog value |
-8000 |
-10V |
-8000 |
-5V |
0 |
0.0V |
-4000 |
-5V |
-4000 |
-2.5V |
4000 |
1.25V |
0 |
0V |
0 |
0V |
8000 |
2.5V |
+4000 |
+5V |
+4000 |
+2.5V |
12000 |
3.75V |
+8000 |
+10V |
+8000 |
+5V |
16000 |
5.0V |
0V to 10V DC input or output |
0mA to 20mA input or output |
4mA to 20mA output |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Digital value (INT) |
Analog value |
Digital value (INT) |
Analog value |
Digital value (INT) |
Analog value |
0 |
0.0V |
0 |
0.0mA |
0 |
4.0mA |
4000 |
2.5V |
3200 |
4.0mA |
4000 |
8.0mA |
8000 |
5.0V |
6400 |
8.0mA |
8000 |
12.0mA |
12000 |
7.5V |
9600 |
12.0mA |
12000 |
16.0mA |
16000 |
10.0V |
12800 |
16.0mA |
16000 |
20.0mA |
16000 |
20.0mA |
||||
This command description provides basic hardware documentation only. For detailed technical information, consult the manual:

All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header. The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
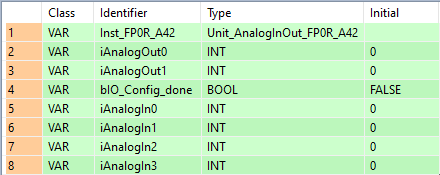
Inst_FP0R_A42(iIOWordOffset := 4,
iOutChannel0 := iAnalogOut0,
iOutChannel1 := iAnalogOut1,
iOutChannel0_Config := 0,
iOutChannel1_Config := 0,
iInChannel0_Config := 0,
iInChannel1_Config := 0,
iInChannel2_Config := 0,
iInChannel3_Config := 0,
bConfigIsDone => bIO_Config_done,
iInChannel0 => iAnalogIn0,
iInChannel1 => iAnalogIn1,
iInChannel2 => iAnalogIn2,
iInChannel3 => iAnalogIn3);
Use ExpansionUnitNumberToIOWordOffset_FP0 or ExpansionUnitNumberToIOWordOffset_FPX_FP0 to calculate the word offset of the analog unit connected to the CPU.
BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 12 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_COMMENT,,FP0R-A42,2,1,17,2,);
B(B_FB,Unit_AnalogInOut_FP0R_A42!,Inst_FP0R_A42,19,1,34,12,,?BiIOWordOffset?BiOutChannel0?BiOutChannel1?BiOutChannel0_Config?BiOutChannel1_Config?BiInChannel0_Config?BiInChannel1_Config?BiInChannel2_Config?BiInChannel3_Config?CbConfigIsDone?CiInChannel0?CiInChannel1?CiInChannel2?CiInChannel3);
B(B_VARIN,,4,17,2,19,4,);
B(B_VAROUT,,bIO_Config_done,34,2,36,4,);
B(B_VARIN,,iAnalogOut0,17,3,19,5,);
B(B_VAROUT,,iAnalogIn0,34,3,36,5,);
B(B_VARIN,,iAnalogOut1,17,4,19,6,);
B(B_VAROUT,,iAnalogIn1,34,4,36,6,);
B(B_VARIN,,0,17,5,19,7,);
B(B_VAROUT,,iAnalogIn2,34,5,36,7,);
B(B_VARIN,,0,17,6,19,8,);
B(B_VAROUT,,iAnalogIn3,34,6,36,8,);
B(B_VARIN,,0,17,7,19,9,);
B(B_VARIN,,0,17,8,19,10,);
B(B_VARIN,,0,17,9,19,11,);
B(B_VARIN,,0,17,10,19,12,);
L(1,0,1,12);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODY
Inst_FP0R_A42(iIOWordOffset := 4,
iOutChannel0 := iAnalogOut0,
iOutChannel1 := iAnalogOut1,
iOutChannel0_Config := 0,
iOutChannel1_Config := 0,
iInChannel0_Config := 0,
iInChannel1_Config := 0,
iInChannel2_Config := 0,
iInChannel3_Config := 0,
bConfigIsDone => bIO_Config_done,
iInChannel0 => iAnalogIn0,
iInChannel1 => iAnalogIn1,
iInChannel2 => iAnalogIn2,
iInChannel3 => iAnalogIn3);