


 FP_GET_IO_START_OFFSET
FP_GET_IO_START_OFFSETGet offset of I/O address
This FP instruction gets the start offset of an I/O address of the slot specified by s_Slot and stores the result in d.
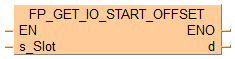
Input
Slot number: 0–64
Output
Offset for the first valid I/O address
We recommend using FP_GET_UNIT_OFFSETS1 to get all offsets from DIX, DIY and DI2 in a standardized way that allows to access all relevant memories of a unit.

All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header. The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
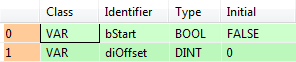
VAR
bStart: BOOL:=FALSE;
diOffset: DINT:=0;
END_VAR
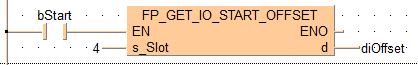
BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
ACTIVE_NETWORK := 0 ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 5 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_F,FP_GET_IO_START_OFFSET!,,8,1,22,5,,?DEN?Ds_Slot?AENO?Cd);
B(B_VARIN,,4,6,3,8,5,);
B(B_VAROUT,,diOffset,22,3,24,5,);
B(B_CONTACT,,bStart,3,2,5,4,);
L(1,3,3,3);
L(5,3,8,3);
L(1,0,1,5);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODY
IF (bStart) then
FP_GET_IO_START_OFFSET(s_Slot :=4, d => diOffset);
END_IF;