


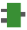 AreaOffs_ToVar
AreaOffs_ToVarCopies the content of an address to a variable with 16-bit offset
This function copies number of words defined by the size of the variable Var to the variable Var from the address determined by the memory area Area and the address offset Offs.
Input
Value for the memory area1)
If Area is a variable, then it must be located in the memory area DT or FL. This should be checked using a function that incorporates the FP Tool Library's functions Is_AreaDT or Is_AreaFL.
Offset for the starting 16-bit address of the memory area
Output
Variable to which the address's content is copied
The values for Area and Offs can be supplied via the function GetPointer. The value for Area has to lie in the DT orFL area.
Flag memory areas Available for FP7 only. |
SYS_MEMORY_AREA_R |
SYS_MEMORY_AREA_L |
|
SYS_MEMORY_AREA_X |
|
SYS_MEMORY_AREA_Y |
|
Flags |
SYS_MEMORY_AREA_WR |
Set value timer/counter |
SYS_MEMORY_AREA_SV |
Elapsed value timer/counter |
SYS_MEMORY_AREA_EV |
Data registers |
SYS_MEMORY_AREA_DT |
Link flags |
SYS_MEMORY_AREA_WL |
Link registers |
SYS_MEMORY_AREA_LD |
File registers |
SYS_MEMORY_AREA_FL |
Input registers |
SYS_MEMORY_AREA_WX |
Output registers |
SYS_MEMORY_AREA_WY |
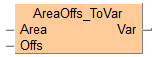
In the global variable list you define variables that can be accessed by all POUs in the project.

Here the variable g_arArrayIn1 is assigned. The variable could just as well be declared In the POU header of the program Program_CalcSums.
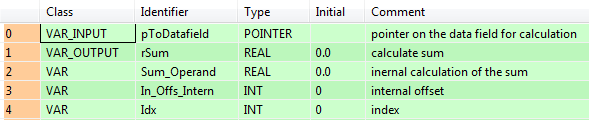
All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header. The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
R_EXTERNAL
WrongAreaArray: ARRAY [0..2] OF REAL:=[10.0,20.0,30.0];
END_VAR
VAR
start: BOOL:=FALSE;
RealArrayIn1: ARRAY [0..5] OF REAL:=[10.0,20.0,30.0,40.0,50.0,60.0];
RealArrayIn2: ARRAY [0..3,1..4] OF REAL:=[10.0,20.0,30.0,40.0,50.0,60.0,70.0,80.0,90.0,100.0,110.0,120.0,130.0,140.0,150.0,160.0];
RealArrayIn3: ARRAY [0..2,1..3,2..5] OF REAL:=[10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0];
RealSum1: REAL:=0.0;
(*Result: 210*)
RealSum2: REAL:=0.0;
(*Result: 1360*)
RealSum3: REAL:=0.0;
(*Result: 180*)
IsWrongArea: BOOL:=FALSE;
WrongAreaSum: REAL:=0.0;
CalcSum_Real1: CalcSum_REAL;
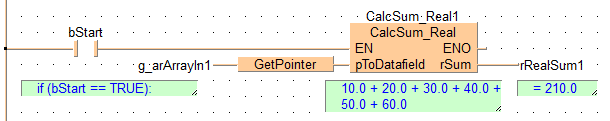
END_VARWhen the variable bStart is set to TRUE, the function block CalcSum_REAL is carried out. It calculates the sum of all elements of the data field g_arArrayIn1 and writes the result to the variable rRealSum1.
BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
ACTIVE_NETWORK := 0 ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 3 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_COMMENT,,This program calculates the sum of all array elements of the input array In,3,1,38,2,);
L(1,0,1,3);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 10 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_VARIN,,start,6,0,8,2,);
B(B_VAROUT,,RealSum1,36,4,38,6,);
B(B_VARIN,,RealArrayIn1,8,2,10,4,);
B(B_FB,CalcSum_REAL,CalcSum_Real1,25,2,36,8,,?BEN?BIn_Area?BIn_Offset?BNrOfIdx?AENO?ASum);
B(B_F,AreaOffs_OfVar,,10,1,22,5,,?D@'Var'?CArea?COffs);
B(B_F,Elem_OfArray1D,,10,5,22,8,,?DArray1D?CNrOfElem1);
B(B_COMMENT,,10+20+30+40+50+60,26,8,35,9,);
B(B_COMMENT,,=,36,8,38,9,);
B(B_COMMENT,,210.0,39,8,43,9,);
B(B_COMMENT,,if (Enable==TRUE):,15,8,25,9,);
L(25,1,25,4);
L(8,1,25,1);
L(24,3,24,5);
L(23,4,23,6);
L(24,5,25,5);
L(10,3,10,7);
L(22,3,24,3);
L(22,4,23,4);
L(22,7,25,7);
L(23,6,25,6);
L(1,0,1,10);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 13 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_VARIN,,start,6,0,8,2,);
B(B_VAROUT,,RealSum2,36,4,38,6,);
B(B_VARIN,,RealArrayIn2,8,2,10,4,);
B(B_FB,CalcSum_REAL,CalcSum_Real1,25,2,36,8,,?BEN?BIn_Area?BIn_Offset?BNrOfIdx?AENO?ASum);
B(B_F,Elem_OfArray1D,,10,5,22,8,,?DArray1D?CNrOfElem1);
B(B_COMMENT,,10+20+30+40+ø^50+60+70+80+ø^90+100+110+120+ø^130+140+150+160,26,8,35,12,);
B(B_COMMENT,,=,36,8,38,9,);
B(B_COMMENT,,1360.0,39,8,43,9,);
B(B_COMMENT,,if (Enable==TRUE):,15,8,25,9,);
L(25,1,25,4);
L(8,1,25,1);
L(24,3,24,5);
L(23,4,23,6);
L(24,5,25,5);
L(10,3,10,7);
L(22,7,25,7);
L(23,6,25,6);
L(1,0,1,13);
L(10,3,24,3);
L(10,4,23,4);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODY
All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header.The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
R_EXTERNAL
WrongAreaArray: ARRAY [0..2] OF REAL:=[10.0,20.0,30.0];
END_VAR
VAR
start: BOOL:=FALSE;
RealArrayIn1: ARRAY [0..5] OF REAL:=[10.0,20.0,30.0,40.0,50.0,60.0];
RealArrayIn2: ARRAY [0..3,1..4] OF REAL:=[10.0,20.0,30.0,40.0,50.0,60.0,70.0,80.0,90.0,100.0,110.0,120.0,130.0,140.0,150.0,160.0];
RealArrayIn3: ARRAY [0..2,1..3,2..5] OF REAL:=[10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0,10.0,0.0];
RealSum1: REAL:=0.0;
(*Result: 210*)
RealSum2: REAL:=0.0;
(*Result: 1360*)
RealSum3: REAL:=0.0;
(*Result: 180*)
IsWrongArea: BOOL:=FALSE;
WrongAreaSum: REAL:=0.0;
CalcSum_Real1: CalcSum_REAL;
END_VAR
Network 1:
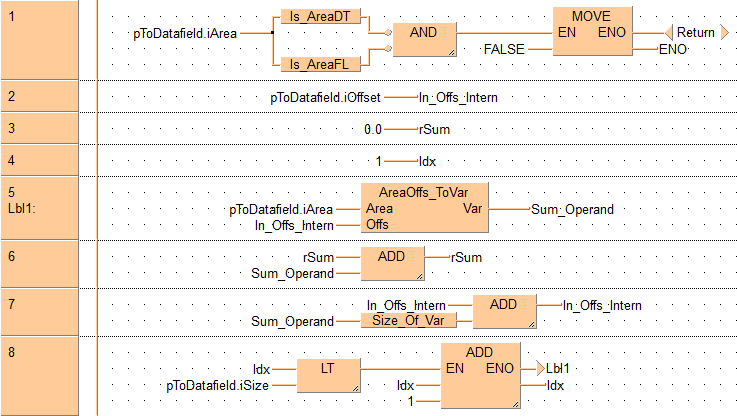
If the data field delivered does not lie in the DT or FL area, the ENO of the function block is set to FALSE and the processing ended.
Network 2: 4:
Here the initializations for calculating the sum that follows is dealt with. Since variables of the class VAR_INPUT cannot be changed directly, the input variable In_Offset has to be copied to the internal variable In_Offs_intern.
see also: Var_ToAreaOffs
Network 5: 8:
Loop for the sum calculation.
BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
ACTIVE_NETWORK := 0 ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 3 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_COMMENT,,This program calculates the sum of all array elements of the input array In,3,1,38,2,);
L(1,0,1,3);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 10 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_VARIN,,start,6,0,8,2,);
B(B_VAROUT,,RealSum1,36,4,38,6,);
B(B_VARIN,,RealArrayIn1,8,2,10,4,);
B(B_FB,CalcSum_REAL,CalcSum_Real1,25,2,36,8,,?BEN?BIn_Area?BIn_Offset?BNrOfIdx?AENO?ASum);
B(B_F,AreaOffs_OfVar,,10,1,22,5,,?D@'Var'?CArea?COffs);
B(B_F,Elem_OfArray1D,,10,5,22,8,,?DArray1D?CNrOfElem1);
B(B_COMMENT,,10+20+30+40+50+60,26,8,35,9,);
B(B_COMMENT,,=,36,8,38,9,);
B(B_COMMENT,,210.0,39,8,43,9,);
B(B_COMMENT,,if (Enable==TRUE):,15,8,25,9,);
L(25,1,25,4);
L(8,1,25,1);
L(24,3,24,5);
L(23,4,23,6);
L(24,5,25,5);
L(10,3,10,7);
L(22,3,24,3);
L(22,4,23,4);
L(22,7,25,7);
L(23,6,25,6);
L(1,0,1,10);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 13 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_VARIN,,start,6,0,8,2,);
B(B_VAROUT,,RealSum2,36,4,38,6,);
B(B_VARIN,,RealArrayIn2,8,2,10,4,);
B(B_FB,CalcSum_REAL,CalcSum_Real1,25,2,36,8,,?BEN?BIn_Area?BIn_Offset?BNrOfIdx?AENO?ASum);
B(B_F,Elem_OfArray1D,,10,5,22,8,,?DArray1D?CNrOfElem1);
B(B_COMMENT,,10+20+30+40+ø^50+60+70+80+ø^90+100+110+120+ø^130+140+150+160,26,8,35,12,);
B(B_COMMENT,,=,36,8,38,9,);
B(B_COMMENT,,1360.0,39,8,43,9,);
B(B_COMMENT,,if (Enable==TRUE):,15,8,25,9,);
L(25,1,25,4);
L(8,1,25,1);
L(24,3,24,5);
L(23,4,23,6);
L(24,5,25,5);
L(10,3,10,7);
L(22,7,25,7);
L(23,6,25,6);
L(1,0,1,13);
L(10,3,24,3);
L(10,4,23,4);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODYFurther example projects (directory "Samples" of FPWIN Pro installation):
Calculates the product of two-dimensional arrays