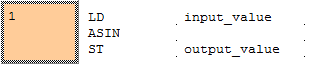 ASIN
ASINArcsine
ASIN calculates the arcsine of the input variable and writes the angle data in radians into the output variable. The function returns a value from - p/2 to p/2.
Input
Input value between -1 and +1
Output
Output as input: arcsine of input value in radians
if input variable does not have the data type REAL, LREAL or input variable is not ³ -1.0 and £ 1.0
if input variable does not have the data type REAL, LREAL or input variable is not ³ -1.0 and £ 1.0
if output variable is zero
if processing result overflows the output variable

All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header. The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
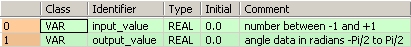
VAR
input_value: REAL:=0.0;
(*range -1 to 1*)
output_value: REAL:=0.0;
(*angle data radians -Pi/2 to Pi/2*)
END_VARThis example uses variables. You can also use a constant for the input variable.

The arc sine of input_value is calculated and written into output_value.
BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
ACTIVE_NETWORK := 0 ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 5 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_F,ASIN!,Instance,7,1,12,3,,?D?C);
B(B_VARIN,,input_value,5,1,7,3,);
B(B_VAROUT,,output_value,12,1,14,3,);
L(1,0,1,5);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODY
output_value:=ASIN(input_value);