


 MOD
MODModular arithmetic division, remainder stored in output variable
MOD divides the value of the first input variable by the value of the second. The remainder of the integral division (e.g. 5 : 2 = 2, remainder = 1) is written into the output variable.

Input
1st input: dividend
2nd input: divisor
Output
Output as input: remainder

All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header. The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
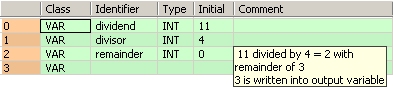
VAR
dividend: INT:=11;
divisor: INT:=4;
remainder: INT:=0;
END_VAR
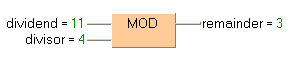
This example uses variables. You may also use constants for the input variables. Dividend (11) is divided by divisor (4). The remainder (3) of the division is written in remainder.
BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
ACTIVE_NETWORK := 0 ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 3 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_F,MOD!,Instance,9,0,14,3,,?D?D?C);
B(B_VARIN,,dividend,7,0,9,2,);
B(B_VARIN,,divisor,7,1,9,3,);
B(B_VAROUT,,remainder,15,0,17,2,);
L(14,1,15,1);
L(1,0,1,3);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODY
remainder:= dividend MOD divisor;