


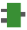 FP_MODBUS_MASTER
FP_MODBUS_MASTERWrite data to slave or read data from slave
Use this instruction to write data from a master to a slave or read data from a slave via the communication port using the Modbus RTU protocol, as defined in the system registers of the port used. Make sure the same protocol is set for master and slave.
Input
Specifies the communication ports depending on the PLC type:
COM port e.g. SYS_COM0_PORT
Ethernet port e.g. SYS_ETHERNET_USER_CONNECTION_1
MCU/SCU e.g. 16#xx01 (xx = slot number) in COM01
Station number of the slave
For FP7 only:
Function codes 05, 06, 15, 16: 0–247
When SCU is used and "0" is specified for the slave unit number, a global transfer is executed. In this case, there is no response message from the slave unit.
Function codes 01, 02, 03, 04: 1-247
For other PLCs:
Function codes 05, 06, 15, 16: 0–99
When "0" is specified for the slave unit number, a global transfer is executed. In this case, there is no response message from the slave unit.
Function codes 01, 02, 03, 04: 1-99
Set to 1, if a SYS_ETHERNET_USER_CONNECTION_xx is applied to input Port
SYS_MODBUS_03_READ_HOLDING_REGISTER
Starting address (0–65535). The address type depends on the command specified by FunctionCode*.
Number of transmission bits or words.
1 for function codes 05, 06
1–2040 for function codes 01, 02
2–2040 for function code 15
1–127 for function codes 03, 04
2–127 for function code 16
Source address on the master for the data to be written to the slave.
Output
For FP7 only: For a description of all error codes, please refer to the table of Modbus/MEWTOCOL communication error codes.
For other PLCs: set to 0

While sending: Master communication sending flag is TRUE
Sending done: Master communication sending flag is FALSE
Normal completion: FALSE
Abnormal completion: TRUE
if the area specified using the index modifier exceeds the limit.
if the area specified using the index modifier exceeds the limit.
When you apply this constant to the input parameter FunctionCode*, the corresponding Modbus command is executed.
For the special case that the connected slave is a Panasonic PLC configured as Modbus RTU slave via system register, one or multiple bits are read from:
Y (Output)
R (Internal flags)
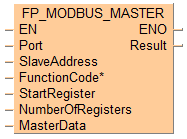
Executing Modbus command 01: reads 1 bit from a Modbus slave beginning at start register 56 set by the variable StartRegister. Then the command stores the 1 bit in the master beginning at the address set by the variable bBool2. The slave's address is converted to a device-specific address depending on the Modbus specifications of the device.
If the connected slave is a Panasonic PLC, the start register 56 corresponds to output Y38 (3*16+8=56).
When you apply this constant to the input parameter FunctionCode*, the corresponding Modbus command is executed.
For the special case that the connected slave is a Panasonic PLC configured as Modbus RTU slave via system register, one or multiple bits are read from:
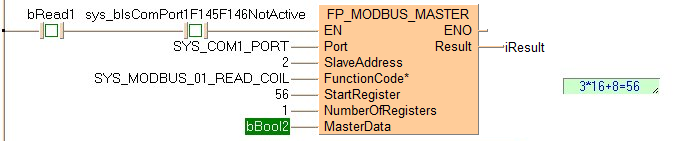
Executing Modbus command 02: reads 1 bit from a Modbus slave beginning at start register 66 set by the variable StartRegister. Then the command stores the 1 bit in the master beginning at the address set by the variable bBool2. The slave's address is converted to a device-specific address depending on the Modbus specifications of the device.
If the connected slave is a Panasonic PLC, start register 66 corresponds to input X42 (4*16+2=66).
When you apply this constant to the input parameter FunctionCode*, the corresponding Modbus command is executed.
For the special case that the connected slave is a Panasonic PLC configured as Modbus RTU slave via system register, one or multiple bits are read from:
Executing Modbus command 03: reads 2 words from a Modbus slave beginning at start register 100 set by the variable StartRegister. Then the command stores the 2 words in the Modbus master 2 beginning at the address set by the variable rCount2. The slave's address is converted to a device-specific address depending on the Modbus specifications of the device.
If the connected slave is a Panasonic PLC, start register 100 corresponds to data register DT100.
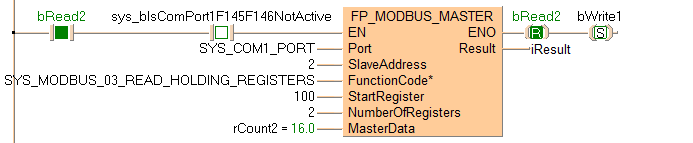
Maximum number of registers: 127.
When you apply this constant to the input parameter FunctionCode*, the corresponding Modbus command is executed.
For the special case that the connected slave is a Panasonic PLC configured as Modbus RTU slave via system register, one or multiple bits are read from:
WL0–WL127 (Link flags)
LD0–LD256 (Link registers)
Executing Modbus command 04: reads 7 words from a Modbus slave beginning at start register 2018 set by the variable StartRegister. Then the command stores the 7 words in the master beginning at LD25 set by the variable MasterData. The slave's address is converted to a device-specific address depending on the Modbus specifications of the device.
If the connected slave is a Panasonic PLC, start register 2018 corresponds to link register LD18.
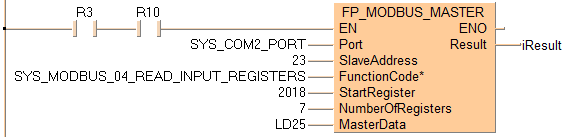
Maximum number of registers: 127.
When you apply this constant to the input parameter FunctionCode*, the corresponding Modbus command is executed.
In case the connected slave is a Panasonic PLC in Modbus RTU mode, one or multiple bits are written to:
Y (Output)
R (Internal flags)
Executing Modbus command 05: writes 1 bit to a Modbus slave beginning at address WY1 set by the variable MasterData. Then the command stores the 1 bit in a Modbus slave beginning at start register 35 set by the variable StartRegister. The slave's address is converted to a device-specific address depending on the Modbus specifications of the device.
If the connected slave is a Panasonic PLC, address 35 corresponds to output Y23 (2*16+3=35).
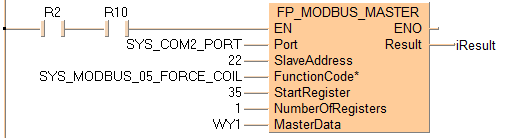
When writing multiple bit data use the SYS_MODBUS_15_FORCE_COILS constant.
Maximum number of register: 1
When you apply this constant to the input parameter FunctionCode*, the corresponding Modbus command is executed.
In case the connected slave is a Panasonic PLC in Modbus RTU mode, one or multiple bits are written to:
Executing Modbus command 06: writes 1 word to a Modbus slave beginning at address DT14 set by the variable MasterData. Then the command stores the 1 word in the Modbus slave beginning at start register 21 set by the variable StartRegister. The slave's address is converted to a device-specific address depending on the Modbus specifications of the device.
If the connected slave is a Panasonic PLC, start register 21 corresponds to data register DT21.
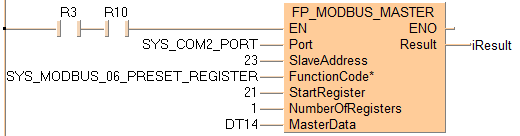
When writing multiple bit data use the SYS_MODBUS_15_FORCE_COILS constant.
Maximum number of register: 1
When you apply this constant to the input parameter FunctionCode*, the corresponding Modbus command is executed.
In case the connected slave is a Panasonic PLC in Modbus RTU mode, one or multiple bits are written to:
Y (Output)
R (Internal flags)
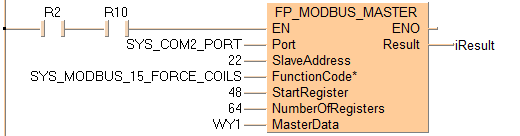
Executing Modbus command 15: writes 64 bits to a Modbus slave beginning at address WY1 set by the variable MasterData. Then the command stores the 64 bits in the Modbus slave beginning at start register 48 set by the variable StartRegister. The slave's address is converted to a device-specific address depending on the Modbus specifications of the device.
If the connected slave is a Panasonic PLC, address 48 corresponds to output Y30 (3*16=48).
When you apply this constant to the input parameter FunctionCode*, the corresponding Modbus command is executed.
In case the connected slave is a Panasonic PLC in Modbus RTU mode, one or multiple bits are written to:
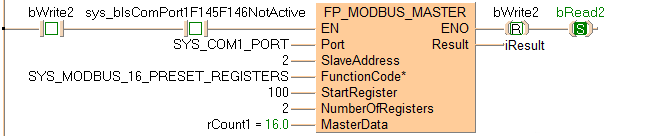
Executing Modbus command 16: writes data to a Modbus slave beginning at the address set by the variable rCount1. Then the command stores the data in the Modbus slave 2 beginning with start register 100 set by the variable StartRegister. The slave's address is converted to a device-specific address depending on the Modbus specifications of the device.
If the connected slave is a Panasonic PLC, start register 100 corresponds to data register DT100.
Maximum number of registers: 127.