


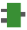 FP_BIN_TO_ASCII
FP_BIN_TO_ASCIIBinary -> ASCII conversion
This FP instruction converts 16-bit/32-bit binary data stored in the area specified by s2_BinaryData to ASCII code. The conversion method is specified by the control string of s1_Format. The converted result is stored in the area specified by d_AsciiData.
Input
Control and format string set in inverted commas
Starting address for storing binary data
Quantity of numbers to be converted: 0–65535
Starting position in ASCII data: 0–255
Output
Starting address for storing ASCII data
Position in the control code |
Description |
s1_Format |
16-bit PLCs |
32-bit PLCs |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Conversion direction |
||||
+ |
forward (only for hexadecimal numbers with specifier x, X) |
'+%4X' |
● |
● |
|
if plus sign is omitted: reverse (default setting) |
'%4X' |
● |
● |
||
 |
% |
format string specifier (mandatory) |
● |
● |
|
 |
Padding format |
||||
0 |
fill with zeros |
'%06x' |
- |
● |
|
+ |
add a plus sign |
'%+4d' |
- |
● |
|
- |
left alignment |
'%-6d' |
- |
● |
|
˽ |
(space) add a space instead of plus sign |
'%˽4d' |
- |
● |
|
# |
insert 0x for hexadecimal numbers |
'%#4X' |
- |
● |
|
append always a decimal point for real number |
'%#8.0f' |
- |
● |
||
 |
8 |
width of the ASCII data element |
'%08d' |
● |
● |
no width
|
'%d,' |
- |
● |
||
 |
Precision after decimal point |
||||
.5 |
any digit after decimal point |
'%8.5f' |
- |
● |
|
 |
I |
double length specifier e.g. specifier i with l = Ii -> DINT |
'+%4ld' |
● |
● |
 |
Format specifier |
||||
i |
INT |
'%10i' |
● |
● |
|
u |
UINT |
'%10u' |
- |
● |
|
d |
INT |
'%6d' |
● |
● |
|
x |
hexadecimal lower case |
'+%4x' |
● |
● |
|
X |
hexadecimal upper case |
'+%4X' |
● |
● |
|
b |
BCD |
'+%5b' |
- |
● |
|
f |
floating-point number |
'+%-6.2f' |
- |
● |
|
e |
exponential 1.23e10 |
'+%9.3e' |
- |
● |
|
E |
exponential upper case 1.23E10 |
'+%9.3E' |
- |
● |
|
g |
floating or exponential |
'+%12g' |
- |
● |
|
G |
floating or exponential upper case |
'+%9.3G' |
- |
● |
|
 |
|
'+%8dPANA' |
- |
● |
|
● available on 16-bit/32-bit PLCs
Example: '+%4X' converts a binary value to a value with a width of four characters in upper case in forward direction (valid for 16-bit/32-bit PLCs)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
16#12A |
'˽12A' |
Example: '%4X' converts a binary value to a value with a width of four characters in upper case in reverse direction (valid for 16-bit/32-bit PLCs)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
16#B2A |
'˽B2A' |
Example: '%06d' converts a binary value to a value with a width of six characters, decimal value with three leading zeros (valid for 32-bit PLCs only)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
16#100 |
'000100' |
Example: '%+4d' converts a binary value to a value with a width of four characters, decimal value, + sign added (valid for 32-bit PLCs only)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
100 |
'+100 ˽ ˽' |
Example: '%-6d' converts a binary value to a value with a width of six characters, left aligned (valid for 32-bit PLCs only)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
100 |
'100˽ ˽ ˽' |
Example: '%˽4d' converts a binary value to a value with a width of four characters with one leading space (valid for 32-bit PLCs only)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
100 |
'˽100' |
Example: '%#8.0f' converts a binary value to a value with a width of eight characters, floating-point number, four leading spaces (valid for 32-bit PLCs only)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
123.45678 |
'˽ ˽ ˽ ˽123.' |
Example: '%8.3f' converts a binary value to a value with a width of eight characters, three characters precision after decimal point (valid for 32-bit PLCs only)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
123.45599 |
'˽123.456' |
Example: '+%10u' converts a binary value to a value with a width of 10 characters, seven leading spaces, unsigned integer (valid for 32-bit PLCs only)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
-100 |
'˽ ˽ ˽ ˽ ˽ ˽ ˽100' |
Example: '%06d' converts a binary value to a value with a width of six characters with three leading spaces (valid for 16-bit/32-bit PLCs)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
100 |
'˽ ˽ ˽100' |
Permissible range for the value before the specifier:
1–15 before specifiers d, ld, i, li |
1–4 before specifier X |
1–8 before specifier lX |
if no width is specified, comma is appended e.g. '%d,' (valid for 32-bit PLCs only)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
100 |
'100,' |
FP_BIN_TO_ASCII: required minimum width is assumed
FP_ASCII_TO_BIN and FP_ASCII_CHECK: comma separator is required
Example: '+%4ld' converts a binary value to a value with a width of four characters, requires DINT or DWORD for the converted result (valid for 16-bit/32-bit PLCs)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
100 |
'˽100' |
Example: '+%6i' converts a binary value to a value with a width of six characters, three leading spaces, signed integer in forward direction (valid for 16-bit/32-bit PLCs)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
-100 |
'˽ ˽ ˽-100' |
Example: '+%6d' converts a binary value to a value with a width of six characters with three leading zeros in forward direction (valid for 16-bit/32-bit PLCs)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
100 |
'000100' |
Example: '+%4X' converts a binary value to a value with a width of four characters, hexadecimal number in upper case in forward direction (valid for 16-bit/32-bit PLCs)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
16#12A |
'˽12A' |
Example: '+%5b' converts a binary value to a value with a width of five characters, BCD data (valid for 32-bit PLCs only)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
16#123 |
'˽123' |
Example: '+%-6.2f' converts a binary value to a value with a width of six characters, left aligned, precision two digits after decimal point (valid for 32-bit PLCs only)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
1.2345 |
'1.23˽' |
Example: '+%9.3e' converts a binary value to a value with a width of 9 characters, precision 3 digits after decimal point, exponential lower case (valid for 32-bit PLCs only)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
1234.5678 |
'1.235e+03' |
Example: '1.235E+03' converts a binary value to a value with a width of 9 characters, precision 3 digits after decimal point, exponential upper case (valid for 32-bit PLCs only)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
1234.5678 |
'1.235E+03' |
Example: '+%12g' converts a binary value to a value with a width of 12 characters, floating-point number (valid for 32-bit PLCs only)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
1234.5678 |
'˽ ˽ ˽ ˽ ˽1234.57' |
Example: '+%9.3G' converts a binary value to a value with a width of nine characters, precision three characters after decimal point, floating-point number, exponential upper case (valid for 32-bit PLCs only)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
1234 |
'˽ ˽ ˽1.E+03' |
For FP_BIN_TO_ASCII: any string can be appended to the conversion
Example: '+%8dPANA' converts a binary value to a value with a width of eight characters, decimal number, 'PANA' is appended (valid for 32-bit PLCs only)
Binary data |
Conversion result in ASCII data |
|---|---|
100 |
'˽ ˽ ˽ ˽ ˽100PANA' |
if there is an error in the control string specified by sFormat.
if forward direction (+) is specified in sFormat when the format is decimal.
if the number of ASCII characters per converted unit specified by n_Conversions exceeds 4 for 16-bit data or 8 for 32-bit data when hexadecimal format is specified by s1_Format.
if 0 is specified for the no. of 16- or 32-bit (1- or 2-word) units to be converted in n_Conversions.
if the number of 16- or 32-bit decimal numbers to be converted specified by n_Conversions exceeds the area for storing ASCII data.
if the converted result exceeds the area.
if there is an error in the control string specified by sFormat.
if forward direction (+) is specified in sFormat when the format is decimal.
if the number of ASCII characters per converted unit specified by n_Conversions exceeds 4 for 16-bit data or 8 for 32-bit data when hexadecimal format is specified by s1_Format.
if 0 is specified for the no. of 16- or 32-bit (1- or 2-word) units to be converted in n_Conversions.
if the number of 16- or 32-bit decimal numbers to be converted specified by n_Conversions exceeds the area for storing ASCII data.
if the converted result exceeds the area.

All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header. The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
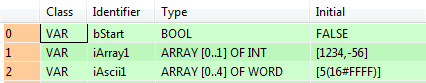
VAR
bStart: BOOL:=FALSE;
iArray1: ARRAY [0..1] OF INT:=[1234,-56];
iAscii1: ARRAY [0..4] OF WORD:=[5(16#FFFF)];
END_VARWhen the variable bStart changes from FALSE to TRUE, the function is carried out. It converts two 16-bit units to 2 x 4 decimal ASCII data. Offset = 1 ASCII character (8-bit).

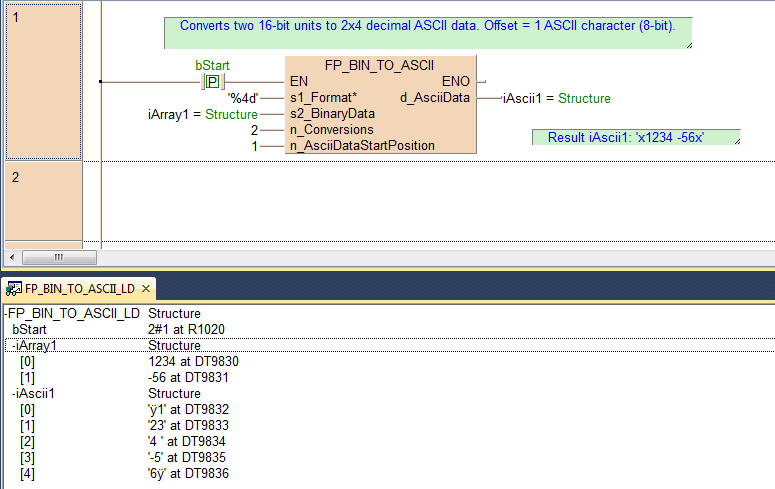
BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
ACTIVE_NETWORK := 0 ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 10 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_VARIN,,'%4d',10,5,12,7,);
B(B_VARIN,,iArray1,10,6,12,8,);
B(B_VARIN,,2,10,7,12,9,);
B(B_VAROUT,,iAscii1,25,5,27,7,);
B(B_CONTACT,,bStart,7,4,9,6,R);
B(B_COMMENT,,Converts two 16-bit units to 2x4 decimal ASCII data. Offset = 1 ASCII character (8-bit).,5,1,38,3,);
B(B_F,FP_BIN_TO_ASCII!,,12,3,25,10,,?DEN?hs1_Format?ds2_BinaryData?dn_Conversions?dn_AsciiDataStartPosition?AENO?cd_AsciiData);
B(B_VARIN,,1,10,8,12,10,);
B(B_COMMENT,,Result iAscii1: 'x1234 -56x',28,8,41,9,);
L(9,5,12,5);
L(1,5,7,5);
L(1,0,1,10);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODY
IF DF(bStart) then
FP_BIN_TO_ASCII(s1_Format := '%4d',
s2_BinaryData := iArray1,
n_Conversions := 2,
d_AsciiData => iAscii1);
END_IF;