


 LEN
LENString length
LEN calculates the length of the input string and writes the result into the output variable.

Input
input data type
Output
length of string
If this instruction is used with UTF-8 strings, please refer to the notes concerning UTF-8 strings under the data type STRING.
If the strings are longer than the length defined for the input variables (IN1 and IN2) in the declaration field “Type”, an error occurs (see sys_bIsCarry for error handling).
if a string applied at the input or output is an invalid string
if a string applied at the input or output is an invalid string

All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header. The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
VAR
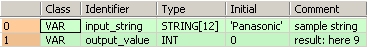
input_string: STRING[12]:='Panasonic';
(*sample string*)
output_value: INT:=0;
(*result: here 9*)
END_VARIn this example the input variable (input_string) has been declared. Instead, you may enter the string ('Panasonic') directly into the function. The string has to be put in inverted commas, both in the POU header and in the function.
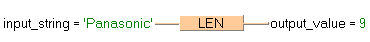
The length (9) of input_string ('Panasonic’) is written into output_value.

BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
ACTIVE_NETWORK := 0 ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 2 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_F,LEN!,Instance,9,0,14,2,,?DIN?C);
B(B_VARIN,,input_string,7,0,9,2,);
B(B_VAROUT,,output_value,14,0,16,2,);
L(1,0,1,2);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODY
output_value:=LEN(input_value);LD |
input_value |
LEN |
|
ST |
output_value |