


 F385_Positioning_WriteData_Backup
F385_Positioning_WriteData_BackupWrite positioning parameters with backup
This instruction is used to write the following positioning parameters and positioning table data with user programs:
General information such as channels/axes used, repetition numbers, and error codes
Axis information such as current execution status and current repetition number
Axis setting information such as pulse output control codes, home return settings, and speed, acceleration and deceleration settings
Positioning table data such as control codes and patterns, speed, acceleration and deceleration settings
This instruction writes the number of words (n_Number) of the data stored in the area starting with s2_Start and stores it in the positioning memory area starting with d_Offset. To keep the written data even after the power has been turned off, the data can additionally be backed up in a persistent memory area.

Input
Channel number
Configurator PMX: SYS_PMX_CHANNEL_0–SYS_PMX_CHANNEL_3
Configurator PM7: SYS_PM7_AXIS_1–SYS_PM7_AXIS_8
Starting address of operation memory areas in the CPU in which the data to be written are stored (source address)
Number of words to be written
Positioning memory area:
Starting address offset of the positioning memory in the CPU for storing data written (destination address)
TRUE: Data is backed up in the hold area
When specifying 16#80 to 16#83 (Save in FROM) for the higher 8 bits of input parameter s1_Channel (the most significant bit is 1), specified data is written into the CPU's FROM. Writing to FROM can be performed up to 10000 times. We recommend using a rising edge to prevent the writing to FROM from being executed continuously.
FALSE: Data is not backed up
if the channel number specified at s1_Channel is invalid
if the positioning memory offset specified at d_Offset exceeds the limit of the positioning area
if the channel number specified at s1_Channel is invalid
if the positioning memory offset specified at d_Offset exceeds the limit of the positioning area

All input and output variables used for programming this function have been declared in the POU header.The same POU header is used for all programming languages.
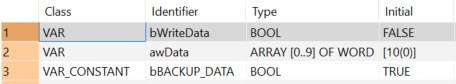
VAR
bWriteData: BOOL:=FALSE;
awData: ARRAY [0..9] OF WORD:=[10(0)];
END_VAR
VAR CONSTANT
bBACKUP_DATA: BOOL:=TRUE;
END_VAR
VAR
END_VAR
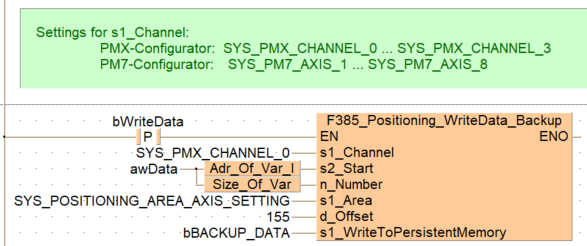
When the variable bWriteData changes from FALSE to TRUE, the function is carried out.
BODY
WORKSPACE
NETWORK_LIST_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
END_WORKSPACE
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 7 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_COMMENT,,ø^Settings for s1_Channel:ø^ PMX-Configurator: SYS_PMX_CHANNEL_0 ... SYS_PMX_CHANNEL_3ø^ PM7-Configurator: SYS_PM7_AXIS_1 ... SYS_PM7_AXIS_8ø^,2,1,49,6,);
L(1,0,1,7);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
NET_WORK
NETWORK_TYPE := NWTYPELD ;
NETWORK_LABEL := ;
NETWORK_TITLE := ;
NETWORK_HEIGHT := 9 ;
NETWORK_BODY
B(B_CONTACT,,bWriteData,9,1,11,3,R);
B(B_F,F385_Positioning_WriteData_Backup!,,20,0,37,9,,?DEN?Ds1_Channel?Ds2_Start?Dn_Number?Ds1_Area?Dd_Offset?Ds1_WriteToPersistentMemory?AENO);
B(B_VARIN,,SYS_PMX_CHANNEL_0,18,2,20,4,);
B(B_VARIN,,awData,11,3,13,5,);
B(B_F,Adr_Of_Var_I!,,13,3,20,5,,?D?C);
B(B_F,Size_Of_Var!,,13,4,20,6,,?D?C);
B(B_VARIN,,SYS_POSITIONING_AREA_AXIS_SETTING,18,5,20,7,);
B(B_VARIN,,155,18,6,20,8,);
B(B_VARIN,,bBACKUP_DATA,18,7,20,9,);
L(1,0,1,9);
L(1,2,9,2);
L(11,2,20,2);
L(13,4,13,5);
END_NETWORK_BODY
END_NET_WORK
END_BODY
(*Settings for s1_Channel:
PMX-Configurator: SYS_PMX_CHANNEL_0 ... SYS_PMX_CHANNEL_3
PM7-Configurator: SYS_PM7_AXIS_1 ... SYS_PM7_AXIS_8*)
if DF(bWriteData) then
F385_Positioning_WriteData_Backup(s1_Channel := SYS_PMX_CHANNEL_0,
s2_Start := Adr_Of_Var(awData),
n_Number := Size_Of_Var(awData),
s1_Area := SYS_POSITIONING_AREA_AXIS_SETTING,
d_Offset := 155,
s1_WriteToPersistentMemory := bBACKUP_DATA);
end_if;